What is SAP Data Archiving?
SAP data archiving is the process of securely removing infrequently accessed data from the SAP database and storing it in an external archive. This helps manage data growth, improve system performance, and ensure legal compliance—without permanently deleting the data.
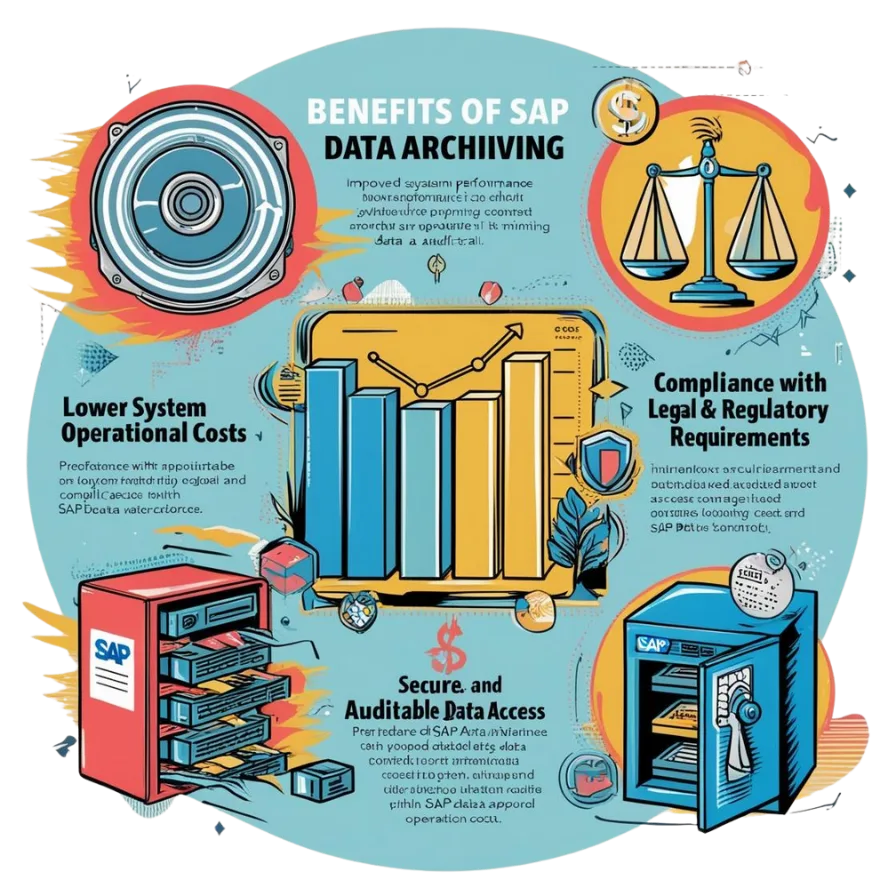
Benefits of sap data archiving
Improved System Performance
Reduces the size of database tables, making queries and transactions faster.
Speeds up backups, restores, and upgrades.
Lower Operational Costs
Decreases the capacity need for expensive database storage (disk or memory for SAP HANA).
Reduces infrastructure costs (e.g., CPU, memory, storage usage) thus cloud costs.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Ensures long-term retention of data per legal mandates. Helps avoid penalties due to improper data handling or loss.
Archived data remains accessible via SAP using archive info structures and reporting tools.
Easier Data Management
Simplifies database maintenance. Makes it easier to manage data lifecycle (e.g., what to retain, archive, or delete).
Minimizes downtime during SAP version upgrades or system migrations by reducing data volume.
TYPES of SAP Data Archiving
Technical Data Archiving
SAP Technical Data Archiving refers to the process of archiving low-level technical or system data that is not related to business transactions, but still consumes space and affects system performance. It complements functional (business) data archiving, but focuses on technical logs and background data.
Some examples: Application logs, IDocs, spool requests, change documents, workflow logs.
Functional Data Archiving
SAP Functional Data Archiving is the process of archiving business-related transactional data from SAP systems that is no longer actively used but must be retained for legal, operational, or analytical purposes.
Some examples: Sales orders, purchase orders, financial documents, HR data, etc.
Customer Table Archiving
SAP Customer Table Data Archiving refers to the process of archiving custom-developed (Z-table) data that resides in tables created specifically for a company’s unique business requirements. These are not standard SAP tables, but rather ones added during SAP customizations or enhancements.
Our Workflow
Modern Approach & Sustainable Results
1.
Project Preparation
- Define scope: What data (modules, objects, tables) will be archived?
- Set objectives: Performance? Compliance? Storage savings?
- Identify stakeholders: Business, IT, audit/compliance, and SAP Basis teams.
- Review retention policies and legal requirements.

2.
Data Analysis
- Use tools like SAP Data Volume Management (DVM) or DB02/DB15 to:
- Analyze data growth trends.
- Identify large tables and archiving potential.
- Evaluate what can be archived vs. deleted.
- Involve business users to define data aging criteria (e.g., completed orders > 3 years old).
3.
Archiving Object Setup
- Use transaction SARA to configure archiving objects.
- For standard objects, SAP provides ready-to-use configurations.
- For custom tables, create archiving objects using AOBJ and ADK.

4.
Test Archiving Process
- Run archiving in a sandbox or development system.
- Validate:
- Archived data correctness.
- Access to archived data via reports (Standard and Custom Reports) or Archive Information Structures (AIS).
- That active processes are not disrupted.

5.
Execute in Production
- Start with a pilot phase (limited data set).
- Schedule archiving jobs using background processing (SM36/SM37).
- Monitor system performance and data space savings.
6.
Archive Storage & Access
- Store archive files on a secure location or content server.
- Implement ArchiveLink if integration with DMS or external storage is needed.
- Ensure read-only access is available for audits or reporting.

7.
Reporting and Validation
- Set up archive info structures (via SARI) to allow searching/reporting on archived data.
- Involve auditors to validate compliance with retention policies.
- Periodically review what else can be archived.
8.
Documentation & Governance
- Document:
- Objects archived
- Retention rules
- Storage location
- Access methods
- Define ongoing archiving schedules (e.g., monthly, quarterly).
- Integrate into your data lifecycle management policy.

related blogs & references
Planning your move to SAP S/4HANA? Don’t underestimate the impact of growing data volumes on migration time, performance, and storage costs. Effective data archiving and Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) are
Understanding SAP Data Archiving SAP data archiving is a systematic process that enables organizations to manage their data efficiently by transferring less frequently used data from active databases to an